What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management is all about getting the right products at the right time and place
in the right quantity at the right cost!
- What is a Supply Chain?
- History and Evolution of Supply Chains
- Why must a company understand its Supply Chain?
- eCommerce Supply Chain
- Specialized Chains
- Challenges with Supply Chains
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Core Components of Supply Chain Management
- Core Component #1 - Strategy
- Core Component #2 - Products
- Core Component #3 - Source of Products
- Core Component #3 - Logistics
- Core Component #4 - Returned Goods
- Different Roles of Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Models
- Why is Supply Chain Management important?
- Supply Chain vs Logistics
- What is Supply Chain Optimization?
- What is the Bullwhip Effect in the Supply Chain?
- Best practices in Supply Chain Management
- Top Supply Chain Trends to Watch in 2021
1. What is a Supply Chain?
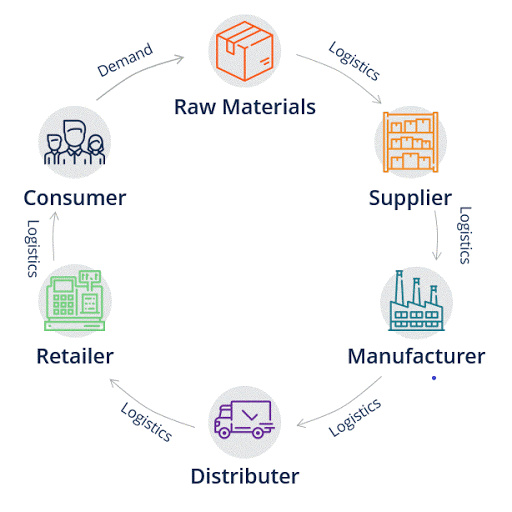
A supply chain is a network of organizations, processes, and people who build and distribute finished products to the end consumers. It includes everyone right from vendors, logistics companies, third-party warehouses, and thus, it is a major cost center.
Source: cdn.corporatefinanceinstitute.com/assets/Supply-Chain-Example.png
In short, it is a network between an enterprise and its suppliers to manufacture and distribute a specific product or service from the earliest stage of sourcing the raw materials to the last-mile delivery of the same to its final buyer. It can be further simplified as a sequence of events that helps a commodity (or service) move from manufacturing (original state) to market (finished product).
A supply chain’s functions may include product development, marketing, operations, distribution, finance, and customer service. In sophisticated supply chain systems, used products may re-enter the supply chain at any point where residual value is recyclable.
Every industry has a supply chain. Supply chains traditionally were straight-line models that looked something like the one illustrated in the picture above. But in the modern world, with such fierce competition, such linear and simple chains are insufficient for maximizing the company’s yield, and getting the supply chain right can either make or break a company. To this end, companies develop complex supply chains that are spread across the globe to reduce their costs and remain competitive in the business landscape. Such supply chains look like a web with the manufacturer in the middle of the web and supply and logistics, forming the web’s trusses.
The fundamental steps of any supply chain are as follows:
- Sourcing of raw materials.
- Transforming these raw materials into basic parts.
- Assembling basic parts to create a final product.
- Order fulfillment or Sales.
- Product delivery.
- Customer service.
The amount of time taken by any one of these processes from start to completion is known as lead time. Supply chain managers monitor lead time and try to minimize it as much as possible. Supply chains aim to meet customer demands, and to this end, supply chain managers coordinate and optimize the processes at every stage to maximize customer satisfaction. An optimized supply chain can result in lower costs and a faster production cycle, but if a single link breaks down, it can affect the rest of the chain and can prove to be very costly.
With increasing globalization and the efficiency of transporting products from A to B, the costs of doing so decrease, in-turn lowering the final cost to the consumer. While deflation is generally regarded as a negative trait for business, the evolution and increased supply chain efficiencies have played a significant role in curbing inflation.
History and Evolution of Supply Chains
Ancient empires across the world, from Peru to Rome, were thoroughly fascinated by the field of logistics as a field in its own right. They understood its importance for the development of their civilization. All notable civilizations of the past have left their own mark on logistics development by undertaking massive organization efforts such as introducing roads, organized labor, transport, and armies.
From ancient times up until the 1700s, the lack of larger transport options and the high cost of moving goods kept all aspects and elements of a supply chain mostly local. Once shipping capabilities expanded, trade routes established and shipping and port management policies in place, the size of supply chains grew exponentially.
The late 1920s introduced mass production along assembly lines, which laid the foundations for the supply chain management. And the first successful implementation of the same was done by Ford. The capability to mass-produce products with consistency and increased efficiency changed trade and supply chains irreversibly. Although till this point, these traditional supply chains involved just the basic logistic steps of production.
Increasing globalization, outsourcing, and availability of information during the 1980s and 1990s prompted the need for integration of business processes across the entire global supply chain. The emergence of computers, the internet, ERP systems sparked a shift from the traditional supply chains and resulted in the idea of adopting supply chain management. Integration granted companies more visibility in steps following and preceding theirs in the chain and optimizing the entire chain rather than just their local process became a prime focus for the companies.
Why must a company understand its Supply Chain?
Mapping and laying out a supply chain is a critical step in performing an External Analysis in a Strategic Planning Process.
- When a company decides to venture into a new industry it exercises external analysis, which examines factors such as competitive structure, position, dynamics, and history of the industry to understand the complexity of that industry. Its primary purpose is to identify opportunities and threats in an industry.
- The strategic planning process is a process of researching a company and its operating environment to formulate a strategy. It involves identifying and evaluating the data that is relevant to the company’s strategy. The process defines the internal and external environments to be analyzed and the data is evaluated using several analytic methods such as SWOT analysis, value chain analysis.
Clearly laying out the supply chain helps a company define its own market and envision its possible future trajectory. While developing corporate-level strategies, companies are often faced with tough choices regarding inventory and warehouse management, deciding whether to operate a single line of business or entering into multiple related or unrelated industries.
Each stage of a supply chain is an entire industry in itself. A competing company’s supply chain provides you a rough approximation of the number of industries involved in the said business. Their supply chain also provides you an insight into the attractiveness or competitiveness of the industries your company might want to venture into in the near future.
eCommerce Supply Chain
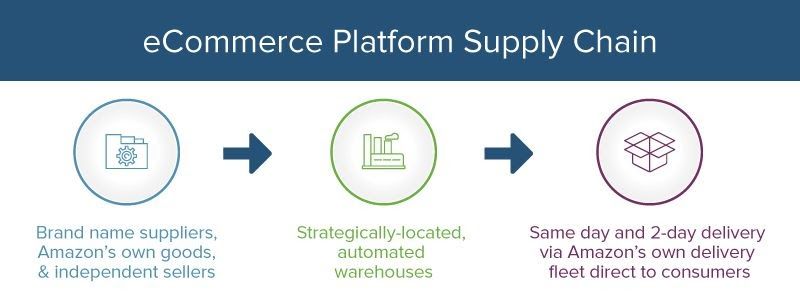
In any generic eCommerce store, whenever a customer places an order, the order is being processed by technologies such as a checkout cart, an order system, or a third-party eCommerce platform for online stores and retail point-of-sale (POS) systems such as Shopify. To deal with payment transactions for the order proprietary or 3rd parties (in most cases) payment processors such as PayPal and Stripe come in. This opens up a new supply chain.
Source: smartsheet.com
A warehouse then receives the order, and the product is readied for delivery and shipping. After shipping, the last mile delivery chain brings the package to the customer’s door.
Any e-commerce shop cuts the retail store out and ships directly to the consumer’s home from distribution centers. Where Amazon stands out is by its innovations in both the supplier end and its final mile chain link – the delivering process. Amazon is a perfect example of unique supply chains.
Because Amazon is a platform and not a shop, just about anyone can sell their merchandise on it; as a result, it has more options available than any other online store.
Their warehouses employ serious eCommerce automation solutions for grouping items going to nearby destinations together. Finally, Amazon does not opt for third-party logistics (3PL) and has made substantial investments in delivery staff and technologies, making 2-day shipping a basic expectation.
Specialized Chains
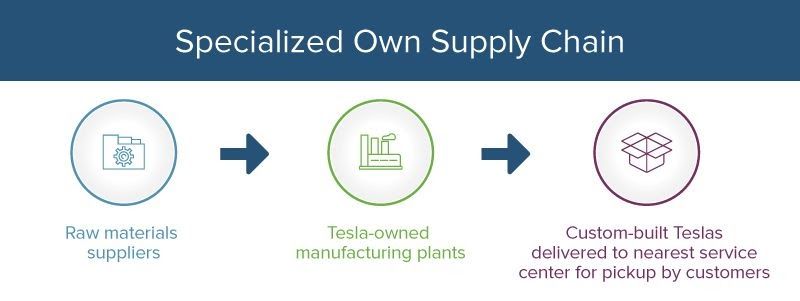
Times have changed since Henry Ford, now, even old-school American carmakers are opening factories abroad. And among this lineage, Tesla is quickly carving a niche for itself and becoming a powerful contender in the automobile manufacturing sector owing to its innovative approaches. Their manufacturing plant is located in California, a location with incredibly costly real estate.
Source: smartsheet.com
Tesla offsets this cost by choosing a vertically integrated supply chain instead of the commonly adopted, long supply chain of cheap part makers. They offer a full-service auto station near its corporate headquarters and also plans for other integrated ventures near the same facility, and Tesla owns it all.
Tesla retains its customers by providing them with a fulfilling experience through their digital supply chain that pushes new firmware and algorithm updates to existing car owners over the cloud.
Challenges with Supply Chains
Modern supply chains are the backbone of every business but their complexity presents several common challenges. These are:
Increased costs throughout the Supply Chain
Rising fuel prices, increasing prices of commodities due to increased prices of raw materials, and higher labor costs throughout the supply chain all contribute to reducing a business’ profit margins. Political policies and protectionism introduce additional tariffs across trade routes that result in shipping delays and increased customs processing time.
Wastage caused by the inadequate production cycle
An inaccurate calculation of a business’ supply, demand, or capabilities may lead to an overstocked inventory that is often a cause of wastage. External factors such as international complexity, economic pressures, and trade disputes all put pressure on the supply chain and make the coordination between elements of a supply chain difficult.
Lack of visibility
Suppliers, manufacturers, logistics, and customers are spread across multiple time zones, countries, and continents. Coordination and management of each element require access to enormous amounts of data, foresight, and planning. Adding each step to the supply chain generates exponential complexity for both upstream and downstream partners.
Lack of visibility and Siloed data increases the difficulty of business intelligence, keeping track, reporting, and good decision-making.
Increasing customer expectations
Consumers have never had more choice, and every customer touchpoint must provide excellent products and services. Retail is no longer the game of lowest pricing when it comes to purchasing goods; quality and speed are quickly becoming just as important. New technologies and businesses have raised customer expectations, making it difficult to manage, and almost impossible to meet.
Delays
Apart from the ones mentioned above, several other miscellaneous factors can cause delays in the supply chain. Missing goods at any point in the chain will ultimately delay the whole process, hamper careful coordination, and negatively impact customers. Currently, there is a shortage of long-haul drivers that are leading to delays in delivery. Increased volumes of internationally-sourced goods result in port congestions. Increasing the waiting duration for ships, trucks, and trains to load, unload, and transfer products.
2. What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply Chain Management is the process of planning, optimizing, and executing a smooth flow of raw materials, finished products, and information across stakeholders. It is an integrated approach that spans over all industry departments, including inventory management, warehousing, production, procurement, sales, marketing, and bookkeeping. This leads to an important observation that communication and insights play a big role in defining the supply chains’ efficiency as data transfer between the corresponding parties is equally important as the goods.
Supply Chain Management is the management of goods and services. It manages the flow of the goods and services and each point of the supply chain until the goods’ end delivery.
The first-ever mention of Supply Chain Management was made by Keith Oliver, a consultant at Booz Allen Hamilton in 1982. Keith had publicly mentioned the term in an interview for Financial Times. Since then, authors and industry leaders have started studying the term and grasping its importance. Nearly a decade later, in the 1990s, books, and novels got published, the importance of Supply Chain Management prominently rose, and many managers started using the term in their job titles. One of the increasing importance of this was it is directly inclined towards inventory management and order management as well. Supply Chain Management became a broader and modern version of traditional logistics.
As previously mentioned, Supply Chain Management is a modern version of logistics. Let me show you the reason behind it. Logistics is an activity that takes place when the transportation of a product. It is mainly limited to a single organization that is dealing with the procurement, maintenance, and inventory. While Supply Chain Management brings together various organizations and they all work together to make the product reach its end destination.
Supply Chain Management can absorb the activities of logistics but not vice versa. Instead, Supply Chain Management is looking after the logistics activities as well as marketing, finances, product development and enhancement, and customer services. Supply Chain Management is, indeed, a wider, broader, and modern term.
3. Core Components of Supply Chain Management
An effective yet simplified Supply Chain Management is incomplete without proper organization. Throughout the years, industry leaders have come up with different combinations of the most important components that make an effective Supply Chain Management. Their hard work has paved the way for today’s working methods.
Supply Chain Management is an integral part of the business and all these elements play an important role in the organization. These functions are also widely known as the integration, operations, purchasing, and distribution stages.
The core components of Supply Chain Management are:
Core Component #1 - Strategy
The art of creating a plan beforehand is called a strategy. Supply Chain Management meticulously plans each and every step of the way for a smooth passage of the product. It makes sure of all the stages involved in the process, brings together all the organizations, and ensures that the goods are seamlessly transported from source to destination.
Integration is also a very big part of the strategy. Integration is a process were bringing together all the parts of the organization and collaborating them to achieve the goal. This way, there is clear transparency, communication between the teams, and smooth operations throughout the organization. Also, due to the integration, there is a clear message about the areas that can be improved or optimized better.
Core Component #2 - Products
Upon creating the strategy, it is important to focus on the products. Make sure that the products that are highly in demand are always available at the warehouse or store. Remember that for quick and efficient supply chain management, it is important to keep the most demanded products in stock as well. It is again, a core component of the same. Customers are always ordering the most demanded products and there are times, when the demand unexpectedly surges, probably due to festivals or occasions or even due to a strong marketing campaign. So, always be prepared round the year for any unexpected activities.
Core Component #3 - Source of Products
Here, the source of the product clearly means where the product is currently available. It can be the manufacturer, storage unit or the warehouse, or a store. Make sure you are aware of the source of the product itself. This way, you will be able to track the product and quickly act upon delivering activities rather than finding a product. It definitely sounds simpler when talking about ‘a’ product, but, this surely helps when companies are dealing with tens of thousands of products at once. Also, to create a product, a number of tools and raw materials are included. Source of the product also includes making sure the raw materials are always available. This way, you can stay one step ahead of the process and are always prepared for the best and the worst.
Core Component #3 - Logistics
Logistics includes the means of transportation. It focuses on the delivery and logistics of the goods. It also includes the means of transportation such as road, sea, air, or rail. While talking about logistics, always make sure that you are aware of the route and delivery methods. This saves ample time and helps establish a smooth logistics method. Companies, these days, focus on lean manufacturing strategies that solely focus on increasing the efficiency of the process. It also includes the monitoring of the process, analyzing the data, and constant improvements in supply chain management.
Core Component #4 - Returned Goods
The sole purpose of returned goods is to ensure that there is proper tracking of the returned goods. There is visibility in the supply chain management and it becomes easier to track the returned goods. The supply chain management process should end when the product reaches its destination, but, in the case of returned goods, the entire cycle restarts in reverse order. A logistics or returned goods software helps you correctly take the right course of action.
4. Different Roles of Supply Chain Management
The popularity of Supply Chain Management has seen a constant uproar since the inception of the term. There was a time when managers added ‘Logistics Manager’ or ‘Fluent in Logistics’ ahead of their titles, these days, people add ‘Supply Chain Management’. Thus, with the increasing demand for the supply chain management term, there have been few important roles added throughout the years.
#1 Chief Procurement Officer (CPO)
A Chief Procurement Officer (CPO) is amongst the highest or most authoritative roles in the business organization. They come under the executive level roles and mainly focus on the procurement and sourcing of goods for a business as a part of a successful supply chain management. They take into consideration key elements such as costs, expenditures, smooth functioning of the procurement process, and ensuring the expenses and errors are to the minimum. Without a doubt, they need to make sure the procurement process is in lieu of the company guidelines and adhering to the internal and external guidelines, including the government laws and regulations.
#2 Chief Logistics Officer (CLO)
A Chief Logistics Officer (CLO) looks after and manages the transportations and logistics process of the supply chain management. They ensure the delivery of goods at each stage of the cycle is smooth. The supply chain management is going seamlessly from receiving the goods until delivering them to their destination. They ensure the correct goods are being shipped, the accuracy of the quantities, and timely delivery of the goods. Apart from this, the CFO also has to take care of the logistics related challenges such as natural (eg.: weather) or manmade interruption, breakdown of the vehicles, or shortage of workforce, tariffs, or taxes. Thus, they support the senior staff and overcome such challenges to ensure the supply chain management is again working in a smooth flow and back to track.
#3 Supply Chain Manager
The main role of a Supply Chain Manager is to create strong collaboration and develop relationships with third-party partners, also known as external parties. This way, they ensure the timely production of the products, calculate the requisite quantities, and generate proper inventory related to the goods, until the products are sold to the market areas or third-party buyers. Their role includes receiving quotations from the suppliers, evaluating their performances, finding their shortcomings, and negotiating with them to finalize a contract. There have been many similarities between a Supply Chain Manager and an Operations Manager; but the main difference between the two are: Supply Chain Managers are focused on external parties and ensuring the products are completed and activities related to them while the Operations Manager focuses more on internal activities related to the operations of the company or that department.
Supply Chain Management has been deemed very important for the business operations and the growth of a company. It also affects shipping management as well as warehouse management. It surely yields a great number of benefits and overcomes its challenges. An effective supply chain management is always possible by digitizing them and introducing technology for proper tracking of the goods and services from inception to delivery. This way, transparency is maintained and the management is aware of the challenges to rectify the errors and opportunities to modify the chain and make it more efficient than ever before.
5. Supply Chain Models
A supply chain model is the supply chain’s operational structure that determines how the stakeholders interact with each other. Like organization structures, it defines the relationships between them as well as their responsibilities. The supply chain model helps understand the dynamics and operating methods for analytical purposes. This helps investors in making financial investment decisions. On the other hand, it helps managers make optimization decisions.
Read more about supply chain models.
6. Why is Supply Chain Management important?
Supply chain management is related to all organizational processes involved in delivering the final product to the end consumer, and hence it impacts efficiency. For instance, the amount of buffer stock is determined by the agility of the supply chain. Having an efficient supply chain will lower the need for stocking the raw materials and buffer stock. Thus, supply chain management has an impact on the overall sustainability and profitability.
Read more about the importance of supply chain management.
7. Supply Chain vs Logistics
Both of these terms look identical and even the people belonging to the industry. However, they are overlapping terms, with logistics being a part of the supply chain. The logistics deal with the individual transfer of goods while the supply chain spans over the entire network.
Read this article to know more about the differences between the supply chain and logistics.
8. What is Supply Chain Optimization?
Supply chain optimization is the process of removing the bottlenecks within the supply chain to improve profitability. This also includes adapting to better operation methods, better tools, and techniques to minimize the waste of resources. The resultant model of the supply chain is generally more agile and dependable despite cutting down on the utilized resources.
Read more about supply chain optimization and its importance.
9. What is the Bullwhip Effect in the Supply Chain?
The bullwhip effect in commerce is misquoting the demand to the suppliers/vendors. Ultimately, each of them adds to the original value only to drastically misquote the initial demand. This is similar to a domino effect, with each block being larger than the previous block. This results in financial losses as the supply exceeds demand, and it can be considered one of the serious problems caused due to poor sales forecasting.
Read more about the bullwhip effect.
10. Best practices in Supply Chain Management
All organizations follow supply chain best practices in varying degrees. However, following a systematic approach across all the departments and coordinating it with the logistics companies can help improve your bottom line. In this section, we will look at the best practices that organizations can easily implement from all sectors. They are oriented towards both improving the individual efficacy as well as efficiency as a whole.
Read more about supply chain management best practices.
11. Top Supply Chain Trends to Watch in 2021
Supply chains are passing through a unique phase when almost the entire market accepts innovative trends. Historically, the supply chain trends were limited to single organizations, with a lack of standardization and interoperability made them obsolete for other businesses. But this is changing for good as we discuss the trends that will make supply chains smarter and more efficient in 2021.
Read about the top supply chain trends to watch in 2021.
PRODUCT
LEARN IN-DEPTH
- Inventory ManagementLearn the essentials of inventory management in this collection of guides.
- Warehouse ManagementLearn the requisites to achieve a fully functional warehouse.
- Order ManagementThe entire life-cycle of order from a fulfillment center to reaching the customer.
- Shipping ManagementGet to know A-to-Z about shipping including its types, important terms, and costs.
- Enterprise Resource PlanningLearn the essentials of Enterprise Resource Planning in this complete guide to ERP.
- Supply Chain ManagementLearn about how supply chain management is all about getting the right products at the right time.
- eCommerce MarketingLearn all about various methods for promoting your online stores to the right target audience.
- Shipping LabelsGet to know everything about shipping labels – its types, how they are made, important terms.
- 3PL CompaniesConnect with all 3PL companies across multi-nations from here.
- Dropshipping CompaniesConsolidated list of Dropshippers internationally for your business
© Copyright 2022 Cin7 Orderhive Inc. All rights reserved. Various trademarks held by their respective owners.




 Back to the table of content
Back to the table of content






