What is Warehouse Management?
Learn to achieve a fully functional and productive warehouse with the help of a cogent super guide
that helps you master all the facets of warehouse management.
- What is a Warehouse?
- What is Warehouse Management?
- Warehousing Roles & Challenges
- Equipment of Warehouse Management
- Benefits of Warehouse Management
- Types Of Warehouses
- Ideal Warehouse Layout & Location
- Type of Warehouse Management
- Warehouse Management Processes
- Calculating Warehouse Performance
- Technologies Used in Warehouse Management
- Safety Concerns in Warehouse
- Warehouse Order Fulfillment Strategies
- Best Practices for Warehouse Management
- Warehouse Management System
- Why should I move from excel to a WMS?
- Why do we need a WMS to manage warehouses?
- Advantages of WMS in the Retail Industry
- How is it different from Inventory Management Software?
- How to select a Warehouse Management System?
- Future of WMS in the retail industry
- Process automation
- Physical Automation
- Warehouse Reports
- 3PL
1. What is a Warehouse?
A warehouse is the backbone of any business because this is where a major amount of investment sits. In fact, the warehouse itself is an investment, and therefore one must know in and out of the warehouse and the products kept in the warehouse.
So let’s start with the definitions of Warehouse –
“A warehouse is a commercial planned place generally used for storage and management of goods in a large proportion.”
While the above one is a simplistic definition an another more elaborate definition of warehouse describes warehouse as
“A facility that provides space, robotic instruments for handling products, storage racks, and a human workforce to manage the incoming goods and outgoing goods. These all things together along with many other small additions make a warehouse that is up and running.”
Also, if you take the business dictionary’s definition into consideration then it says,
“A storage facility within a warehouse management system that is part of a supply chain. The warehouse is located in the most centrally located position to afford a shipping agent the ability to temporarily house shipments for distribution to other warehouse facilities or the final shipping destination.”
What is Warehousing?
Warehousing is the process of storing inventory in a manner that products are easily traceable in a good condition before they are sent into an order fulfillment cycle or sold or distributed to smaller warehouses or retail brick and mortar stores.
Small retailers or startups with fewer funds may have a room or a storeroom as a warehouse, however, large businesses rent big buildings that are designed to store products.
Warehouse vs. Distribution Center
Though the two terms, Warehouse and Distribution center are considered replaceable, however, they are not. A warehouse is a place where goods are stored whereas a distribution center is a place in which not only the products are stored but also are introduced into the order fulfillment process.
2. What is Warehouse Management?
Warehouse Management is about optimizing and controlling the processes of operations and storage of the products in the warehouse right from the moment the inventory enters the facility until it is sold, becomes obsolete, consumed, or moved to another place.
On the other hand, a more discrete explanation of warehouse management present in a research paper on Organizing warehouse management available on research gate says,
“Analogous to production management, the objective of warehouse management is to efficiently and effectively coordinate all warehouse processes and activities. Warehouse management includes all planning and control procedures to operate the warehouse. Planning and control are concerned with managing the ongoing activities of the operations to satisfy customer demand. The main purpose of planning and control is to ensure that operations run effectively and produce products and services as they should.”
The 5 Fundamentals of Warehouse Management
Managing the warehouse isn’t a simple task; it needs to be done with proper planning that rests on some solid fundamental points to be focused on. If you manage your warehouse by keeping these basics in mind, you are sure to reap some great results.
#1 Customer-centric Warehouse Management
It’s pretty much evident that not just your marketing strategies but also your warehouse strategies should be how customers want it. They won’t tell you how you should manage your products. Still, their product preferences and purchase behavior will tell you about what type of inventory you should keep in your warehouse in a way that it’s shipped instantly and doesn’t get delayed due to operational errors whenever the order is placed.
You have to hit the right balance between your productivity and the management of products according to the customers’ choices.
For eg., if you have a combo pack that is being loved by the customers and you are receiving orders at a high rate. Then you will have to streamline warehouse operations in a way that the products in the combo are arranged efficiently and quickly from their warehouse locations to be shipped as soon as possible without any error.
You can provide your customers with a better order fulfillment process if you spend your time shaping your warehousing process in a way that benefits them.
Moreover, the customer-centric approach will provide a smooth hassle-free return or refund policy and a more transparent shipment tracking system for your customers.
#2 Manage your warehouse with a solid workflow and control.
Knowing what should be done is not as tricky as applying that known knowledge of what should be done. If you strategize a plan of action for some departments, you must ensure that the strategy is executed as perfectly as it can be.
To ensure that you need to create proper workflows, processes, rules, and protocols that the warehouse workforce needs to follow so that everybody works in sync and achieves a common goal.
Above is the general warehouse workflow
#3 Create a system that is ready to adapt to the changing circumstances.
Well, workflows, protocols, and rules are essential, but at the same time, being able to change the strategies instantly and work in the direction of the improved strategies is also very important.
It might happen that suddenly your data shows that the trends are changing, and you need to alter your workflow or alter a portion of it. Then, in that case, the entire team, including the warehouse management system, should be able to switch to a different plan of action with as much as less friction as possible.
#4 Data shows you the path.
Don’t make a decision and then see the data; instead, see the data and then make a decision. It is imperative to let your data show you the path, be it the data on customer behavior or the information on your inventory performance.
Even after you have made your decision based on the data, you should always keep your eye on the information/data. Never think that everything will be or is going fine wholly because there will always be one or the other portion that will need improvement. That’s why warehouse management is not a job in which you can relax and let everything run on its own.
#5 Walk with time – Embrace Technology
It’s crucial to keep up with the ever-evolving technology. You never know when the software or a piece of equipment with robotics can be helpful to streamline your warehouse operations or enable you to become an omnichannel e-commerce business.
Companies like Nike pay millions of dollars to predictive analytic firm Boston-based firm “Celect” to design software that can forecast demands.
Software like warehouse and inventory management software, Data accumulation tools, and other robotic instruments can be helpful. Therefore, it’s very much imperative to side with technology for warehouse management. However, you need to be very sure of the technology you implement. It should be useful and be worthy of the money spent on it.
"Inventory vs. Warehouse" Management
Though both the terms have things in common, there’s a fundamental and operational difference between them.
Inventory Management is about managing the stocks in the warehouse and ensuring that the proper flow of stocks is maintained in a supply chain through the order fulfillment process. So, inventory management takes care of and controls the purchases made from suppliers and by customers, storing the stocks, and the entire order fulfillment cycle along with deciding the number of products to be kept available for sale.
Whereas,
Warehouse Management is about managing the whole facility in which the products are stored, including the workforce, the equipment, technology to be used, and the inventory itself. So basically, the job of warehouse management is to create an environment so that the products move fluently through the warehouse.
3. Warehousing Roles & Challenges
As we know, to run a warehouse we, of course, would need an entourage of the human workforce so the table below will give you an idea of the type of workers you would need and what type of roles along with the challenges they will fulfill to help you run a healthy warehouse.
| Designation | Roles | Challenges |
| General Labor |
|
|
| Forklift Driver/Operator |
|
|
| Material Handler |
|
|
| Shipping and Receiving Associate |
|
|
| Shipping Specialist |
|
|
| Loader |
|
|
| Merchandise Pickup/Receiving Associate |
|
|
| Receiver |
|
|
| Warehouse Worker |
|
|
| Stock Clerk (Stocker) |
|
|
| Warehouse Supervisor |
|
|
| Warehouse Manager |
|
|
4. Equipment of Warehouse Management
In modern days, warehouse operation needs a wide array of equipment and if one is intending to have a warehouse of their own then they should know the types of warehouse tools both mechanical and software that would be handy for them. Therefore, the below table will show the types of equipment used in warehouse management.
Dock Equipment
#1 Dock Boards and Plates
The equipment makes it easier and safe for the workers to load and unload the incoming and outgoing stocks.
Image Courtesy – Modern material handling
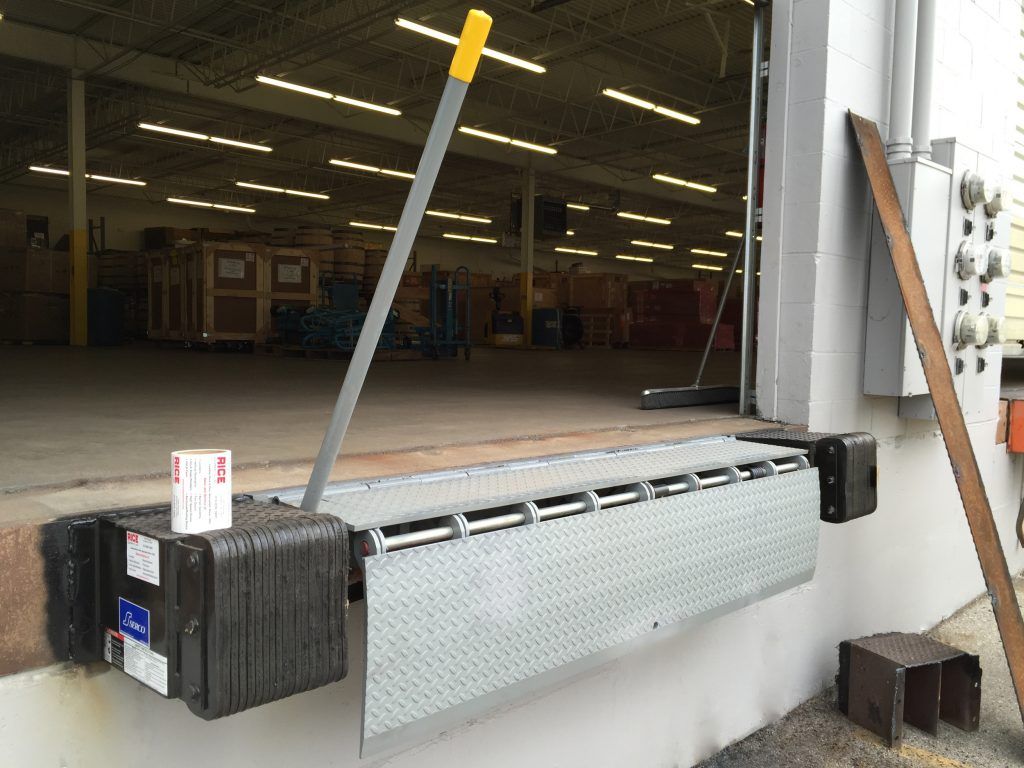
#2 Edge of Docks Levelers
Equipment like dock board & plates and the edge of dock levelers help to bridge the gaps between the trucks and loading dock.
Image Courtesy – Rice equipment co
#3 Truck Restraints
Truck restraints are used to lock the trailers with the docks so that they don’t move while the loading or unloading is done.

Image Courtesy – Kelley Dock leveler
#4 Dock Seals and Shelters
Dock shelters and seals can protect your warehouse and interior loading dock from outside contaminants, and maintain heating and cooling air inside while allowing full access to truck door height and width.

Image Courtesy – Kelley dock leveler
#5 Dock Bumpers
Dock bumpers made of rubbers save boats and trucks from any substantial breakage when they collide with docks.

Image Courtesy – K&R manufacturing
#6 Yard Ramps
Yard ramps, provide a way to load and unload products when the loading dock with the same level is not available. There are also called forklift ramps.

Image Courtesy – Copperloy
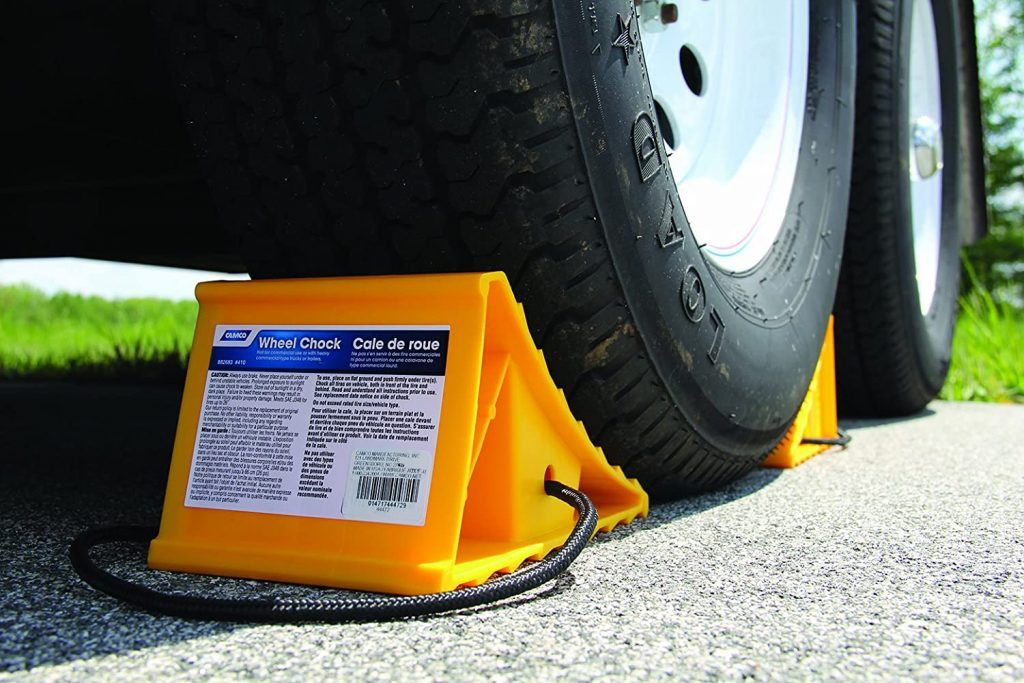
#7 Wheel chocks
Wheel chocks (or chocks) are wedges of sturdy material that are placed closely against a trailer’s wheels to restrict sudden movement while loading or unloading.
#8 Dock lifts and levelers
A dock leveler lift is a lift that is used to bridge the gap between the trailer and dock when the trailer is not able to reach the dock.

Image Courtesy – Kelley dock leveler
Conveyors
Conveyor belts are a boon in warehouse management because a large number of products can be moved from one location to another thus relieving the warehouse workers from lifting and moving heavy products.
Conveyor belts also make the task be completed in a quicker way.
There are several types of conveyors that can be used according to your needs.
#1 Gravity Roller Conveyor
Gravity roller conveyor doesn’t require a motor to move materials and they are usually used when the products are to be moved down an inclined plane or the gravity roller is moved with the help of a person.
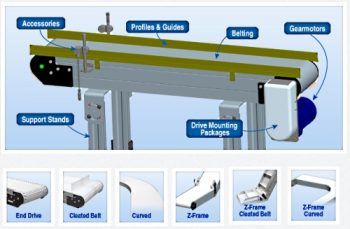
#2 Belt Conveyor
Belt and plastic belt conveyors are the conveyor belts moved with the help of two motorized pulleys.
#3 Flexible Conveyors
Flexible conveyors allow you to change the discharge points by rolling and curving conveyor sections so that they can be fixed anywhere. It’s not a rigid conveyor belt and is very useful in displacing stocks at shipping docks.
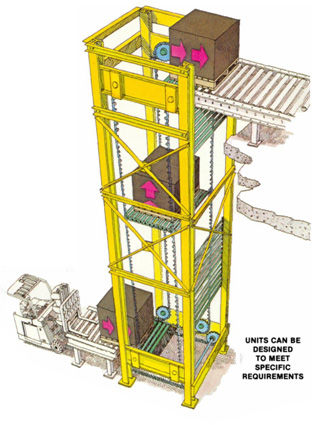
#4 Vertical Conveyors
Vertical conveyor belts are used to displace stocks from one level to another vertical level.
#5 Spiral Conveyors
Spiral conveyor belts are used to transfer the products to different levels without the help of any manual help. They can be installed in places that have less space to accommodate gravity conveyors.
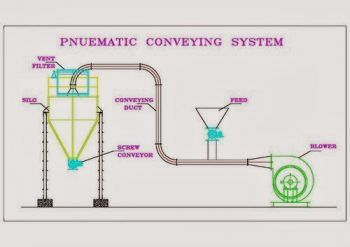
#6 Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic conveyors are used for moving bulk solid, dry, or powder. The pneumatic conveyors are operated with the help of pressurized gas.
#7 Chain Conveyor
Chain conveyors are used to transferring products with the help of chains used as a conveyor that runs a belt.
#8 Dust Proof Conveyors
Dustproof conveyors are belts that resist dust to decrease friction. They can be used to increase productivity and reduce energy consumption.
#9 Automotive Conveyors
Automotive conveyors are programmed motorized conveyors that can weld parts, attach parts with screws, and assemble a vehicle or a machine. These conveyors function on their own once the automation is set.
Storage Equipment
Correct storing equipment helps the warehouse workers to find the products easily. Bins & totes, shelves, racks, and carousels can be used according to your needs.
#1 Bins and Totes
#2 Shelves and Racks
#3 Carousels
Lifting Equipment
Well, lifting equipment is a great help to lift, move, and keep stocks around the warehouse.
#1 Forklifts
Forklifts are basically motorized powerful industrial trucks that are used to lift heavy materials in the warehouse.
#2 Pallet Jacks
Pallet jacks are also used to pick up and move products. Manual pallet jacks are the most basic form of forklifts. Motorized pallet jacks are also in the market.
#3 Hand Trucks
Hand trucks are an L – shaped hand cart.
#4 Service Carts
Service carts can be used to move bins and other products.
#4 Cranes, Hoists, and Monorails
Cranes, hoists, and monorails are the cranes that can be used to pick and transfer materials in a warehouse.
#5 Dollies and Castors
Packing Equipment
Packing equipment is used to weigh and pack the stocks as per the industry standards.
#1 Industrial Scales, Strapping and Banding Equipment
Equipment like Industrial-scale helps in weighing the products, strapping and banding equipment are used to strap and band the products so that the wheel carts can hold the strapping and move with the products.
#2 Stretch Wrap Machines
Stretch wrap machines are used to wrap products instantly without any delay.
#3 Packing Tables
Packing tables as the name suggests are the tables on which the stocks to be wrapped are kept.
Warehouse Robots
Robots are extensively used in warehouse management of large warehouses of large-scale industries.
#1 Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs have been made to replace manual driven forklifts, pallet jacks, etc. They move stocks around the warehouse whenever needed majorly for the purpose of order fulfillment.
#2 Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS)
AS/RS is a group of computer-controlled systems that perform storage and retrieval of products with the help of cranes or shuttles on fixed tracks. They in inventory and warehouse management as they are connected to software that keeps the count of the inventory as well.
#3 Cobots – Collaborative Robots
Cobots are semi-autonomous robots that help humans in completing various tasks. They come with sensors so that they can identify the obstacle and boxes and operate accordingly. They play a huge role in speeding up the order fulfillment process.
#4 Articulated Arm Robots
Articulated arm robots majorly perform picking/packing, receiving/storage, and palletizing of products.
#5 Goods-to-persons (G2P)
Goods-to-person robots (G2P) use automated storage systems and picks the ordered products and put them in front of the human warehouse workers to carry out the fulfillment process.
5. Benefits of Warehouse Management
Warehouse management, if done efficiently, can bring fortunes for your company. Your warehouse and the stock in it are nothing different from the money that is in your account both need to be supervised proficiently or else you can lose money.
This section will inform you about the benefits that you will reap if you manage your warehouse meticulously.
#1 Don’t have to crib for proper space for stock storage.
No one can get enough of the storage space and most warehouse managers crib about not having to strike a balance between adequate stock and finding adequate space for that stock.
Warehouse management aims to create a layout of the warehouse that uses the maximum space of the warehouse horizontally and vertically for the placement of the planned stock in a perfect manner.
#2 You can get the best out of your warehouse employees.
Managing the warehouse also encloses the fact that you have supervised your warehouse employees’ work as well. Warehouse management ensures that you keep your receivers, material handlers, equipment operators, picking and packing associates, and all other stakeholders that are responsible for a warehouse’s smooth operation on their toes by motivating them, allotting tasks, following up on the given tasks, rewarding them for extraordinary work and checking whether they are able to achieve their targets efficiently or not.
#3 Decrease in inventory carrying costs and other unnecessary costs.
Another benefit of warehouse management is that it can help you in controlling the inventory carrying cost by managing the stocks by using different techniques such as ABC analysis, FNS technique, Perpetual and periodic inventory management, Just-in-time, FIFO & LIFO, EOQ, Two bin inventory control, Dropshipping and many other.
With warehouse management, you increase the speed of the order fulfillment process which will eventually impact the stock-flow speed thus reducing the inventory carrying cost and increasing the profits.
Identifying the dead stock and creating a strategy to get rid of it to reduce inventory carrying cost.
#4 Increased Profitability
It is often said that the key to gain that edge over your competitors as far as earning profits is concerned lies in how you manage your warehouse. Your competitor might have more sales than you but if you manage your warehouse proficiently you end up saving a lot of money that you may have otherwise lost in making unnecessary investments and paying for the errors.
#5 Boosted Receiving, picking-packing, order processing speed, and accuracy.
Warehouse management can improve your warehouse operations and order processing speed and accuracy with the use of modern technologies like robots and warehouse automation, inventory and warehouse management software, forklifts, conveyors, and other mechanical and technological equipment.
6. Types Of Warehouses
Types of Warehouses
Warehouses are large-scale storage facilities designed to stack goods efficiently for supply chain purposes. They are classified into the following types based on their application.
#1 Retail Warehouse
Retail warehouses are stores dealing in consumer goods that are operated in single-level buildings. Generally, they are limited to 1000 square meter retail spaces. The floor space is mostly majorly allocated to sales with some of the space also being utilized for back office and storage purposes.
Click here to learn more about ‘Retail Warehouse’
#2 Cold Storage
It is a facility for storing temperature-sensitive goods used for both edible and non-edible products. Moreover, they are control environments to ensure desired quality and usability with humidity, microorganism prevention mechanisms.
#3 Distribution & Fulfillment Warehouse
A distribution warehouse is an intermediary storage facility where manufacturers unload products for distributors to forward to retailers. Thus, they provide cushioning to the supply chain. Fulfillment warehouses are third-party warehouses used by eCommerce companies to control costs and manage strategic benefits. The products are lifted from the seller site and stored here until they are dispatched for delivery after processing.
Click here to learn more about ‘Distribution & Fulfillment Warehouse’
#4 Hazmat Warehouse
This is an abbreviation for the Hazardous Materials Warehouse which is designed to safely store chemicals and physically dangerous substances. It also includes radioactive and biologically dangerous materials. Special provisions are made because these substances can damage their surrounding environment and put lives at risk. In cases of Hazmat warehouses, compliance is also a primary factor in design. Government agencies are involved to ensure safety at such sites.
Compliance regulations regarding layout is also a major parameter as it controls the effective utilization and operational efficiency of the storage facility. Based on the requirements, locations are kept away or near the demand centers. The industries which require such materials often hire 3PL partners if they don’t want to invest in setting up such facilities. Also, non-hazardous and hazardous materials can be stored provided that regulatory norms are met.
7. Ideal Warehouse Layout & Location
The ideal design for any warehouse is dependent on the industry it serves and the local conditions. In cases like the Hazmat warehouses as saw above, laws also govern their layout and construction. Thus, it changes from case to case.
#1 Warehouse layout and location
Since warehouses are used for commercial purposes, their design and infrastructure need to confirm industry standards. The location is usually kept near the demand centers and accessible by transportation facilities.
Click here to learn more about ‘Warehouse layout and location’
#2 Labeling areas of your warehouse
Every area inside the warehouse is identified on the basis of the purpose it serves. The number of racks, storage capacity, and accessibility are used for labeling different areas.
#3 How to organize inventory in your warehouse?
Organizing inventory inside the warehouse is a scientific process. A lot of factors like frequency of movement, accessibility, hazards, and weight define the arrangement of inventory. To learn about some really useful organizing inventory ideas in detail click here.
8. Type of Warehouse Management
Warehouse management is the process of administering and controlling the operations within the warehouse and synchronizing it with the entire supply chain.
Lean warehouse management methods are taking a center stage in the current times due to apparent business advantages as they yield more profit with fewer investments.
Click here to explore more about ‘lean warehouse management methods’.
9. Warehouse Management Processes
All processes involved revolving around the interactions with the inventory. This includes receiving, stacking, and dispatching. However, Cross Docking requires a certain difference in the approach. Adequate documentation is done to develop SOPs and reports for future reference.
Click here to explore more.
Receiving & Put Away
A pre-receipt process is issued when the products are received at the warehouse facility. This includes confirmation with the logistics partner regarding the quantity and usability of the received items. This is followed by proper offloading or cross-docking as required.
Click here to explore more.
Pick Preparations
Once the firm receives an order, the item is picked to fulfill the concerned order. Packaging it according to the item type and mode of transport is done at packing stations. Next, it is shipped through the delivery channel along with appropriate feedback for inventory management. This process also requires integration with logistics partners for smooth functioning.
#1 Picking Strategies: Types of Picking Processes
Picking strategies are oriented towards retrieving the items from different locations inside the warehouse. This includes Discrete, Zone, Wave, and Cluster picking as well as hybrid models formed by combining them.
Click here to learn more.
#2 Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is done in three ways. Small scale operations are managed with the help of CRM solutions while many enterprises go for 3PL partners to fulfill the orders. However, the best alternative available in the market is the use of an integrated warehouse management system as it is tailored to the organization’s needs.
Click here to learn more.
#3 Packing Stations
Once the products are brought for shipping, the items are brought to a central area for packing purposes. The packing stations consist of specialized tables where the workers can pack them. This requires sorting the orders and placing barcodes on the ready-to-ship packages.
Click here to learn more.
#4 Shipping Station
Packing items on the floor isn’t convenient so people started doing it on tables. Later, these tables were modified to provide convenience and better utility. These tables are known as shipping stations. Most of the retailers and warehouses have shipping stations to enhance productivity. These shipping stations are the final stage before the product is handed over to the shipping partners or the courier companies.
#5 Inventory Control
Inventory control is a process of keeping a track of the stock to optimize and maximize one’s warehouse inventory. Inventory control plays a vital role in ensuring that the inventory is tracked with the use of barcode scanners, reorder reports, etc. To manage a warehouse proficiently, a warehouse manager needs to know the stock in and out.
Read in detail about inventory control.
Stock Transfers
When the stock is transferred from one location to another inside the warehouse, documentation regarding the assigned personnel, stock, method of transfer, and entries are made accordingly in the inventory management software.
Click here to learn more.
Move Locations
Moving the warehouse location requires proper analysis for both feasibility and overall market condition. This is a business decision and hence a lot of data is collected before evaluation and taking the final call if not required by a state of emergency. Generally, a plan is devised that encompasses all the factors of relocation and defines the role of each stakeholder. This also includes the backup plans for any mishaps and storage of inventory. Additional inventory is stored at alternate sites so as to meet demands in case the warehouse at the other location isn’t ready in the due time.
Return Merchandise Authorization
When the customers return the product or it is returned because it can’t be delivered, the seller has to verify the reason accordingly. Receiving the returned merchandise is done by following a systematic checking procedure. In case of a claim regarding quality/quantity defect, the concerns are confirmed for further action by the selling platform. Also, the firm shall process the RMA as per documentation laid out by the seller platform to ensure fair judgment for both sides. This is required as the products are either to be sent for repairs or stored for meeting other orders in the future.
10. Calculating Warehouse Performance
From the business point of view, a warehouse is an asset and thus, it is necessary to measure and manage its rate of return. Warehouse performance can be understood as the confirmation of a warehouse to expected financial and operational benchmarks.
| 1. Order Lead Time | 4. Rate of Returns |
| 2. Carrying Cost of Inventory | 5. Perfect Order Rate |
| 3. Inventory Turnover | 6. Picking & Shipping per Hour |
#1 Order Lead Time
Once the order is placed by your firm, the total time required for it to be fulfilled and reach your premises is known as the order lead time. It is crucial for inventory control because the reorder levels are decided on the basis of the lead time and factor of safety (A multiple of the rate of consumption rate for a given time period).
#2 Carrying Cost of Inventory
For a business, the unsold goods not only hold the capital without generating appreciation but also results in the carrying cost. This includes the storage facility’s rent/Morgridge, utility services, and staff. Hence, this metric gives an idea of how long shall the items stay in the warehouse and the corresponding addition to selling costs.
Click here to learn more about ‘Carrying Cost of Inventory’
#3 Inventory Turnover
The inventory turnover ratio, for manufacturing, is the average time for turning raw materials into finished products, and for an online and offline retailer, is the number of times an inventory is sold or purchased. It has a huge impact on a business’s profitability. The rate of inventory turnover is also connected to the efficient use of resources. The higher the turnover, the better is the financial health of the business. To serve this purpose, these metrics give an idea regarding any inefficiencies and also help in the decision-making process.
Click here to learn more about ‘Inventory Turnover’
#4 Rate of Returns
In simple words, it is the percentage return on the invested capital by a business. This includes both tangible and intangible investments that are used in the enterprise to create value. It can also be counted individually for each product to get an overview of profitable ventures.
#5 Perfect Order Rate
The number of orders fulfilled without any damage during the process without any mistakes on a timely basis against total orders is known as the perfect order rate. It is a powerful KPI used for the measurement of effectiveness because it focuses on increasing the effective utilization of capital and client satisfaction. It emphasizes the elimination of all shortcomings like shortage of inventory, late processing of orders and dispatches, and faulty handling. This is pivotal to client satisfaction as a higher perfect order rate reflects the meeting of expectations. Higher Perfect Order Rate also improves the profitability of the company. On the other hand, it can also give hints regarding any problem areas in the work process.
#6 Picking & Shipping per Hour
Once the orders are confirmed, the staff at the warehouse has to pick the products from their respective locations. Picking becomes complex in the cases of product bundling and multi-storeyed warehouses. The average time for picking the items can be reduced by collecting the items in batches. Also, the workers shall consider the size of the item for ensuring optimal collection every time they go for fetching.
Shipping time per item can be reduced by coordinating the multi-product consignments during the picking phase. The use of proper shipping stations also increases the average shipping time per order. Higher picking and shipping per hour are indicators of excellent management and higher efficiency. It also helps in meeting peak demands easily.
11. Technologies Used in Warehouse Management
With the advent of computerized solutions, new cyber-physical solutions took over the manual methods. They improvise the processes by helping companies exercise greater control over their inventories. Business intelligence is also one of the biggest advantages availed by their use.
#1 Barcodes / GTIN Labels
They are used as identification tools that are directly placed on the cartoons/products. They are cheap, effective, and widely used by almost every business today. Barcodes are used at every stage of the supply chain to ensure seamless management.
Click here to learn more about ‘Barcodes / GTIN Labels’
#2 RFID
RFID (Radio-frequency Identification) technology is used in the case of high speed- high precision operations. RFID microchips can function properly up to a range of 100 meters. While they are comparatively costlier than barcodes, they provide higher reliability and are virtually errorless.
#3 Warehouse Robotics
The use of robots is increasing in order to reduce the number of touches. This reduces the mistakes in handling the inventory. It also curbs proliferation and misplacing by employees while saving a considerable amount of time per transaction.
Click here to learn more about ‘Warehouse Robotics’
#4 Internet of Things
As IR 4.0 continues to defy the norms in multiple industries, warehouse owners are taking a step forward by including IoT in their operations. This may radically redefine the way businesses interact with their inventory and the supply chain at large.
12. Safety Concerns in Warehouse
Every other job has a certain amount of risk involved in it and therefore you need to take some safety measures into consideration to keep your employees safe because not only you are bound by law to do that but also as a human and a business owner or manager you need to understand the importance of a skilled worker.
Before talking about the safety procedures you need to go through the type of accidents/safety hazards that your warehouse and the workers working in the warehouse might suffer.
- Accidental fires due to naked electric wires, chemical leakages, or any other inflammable material catching fire. These type of mishaps not only cause fatalities to workers but also has the potential to damage the warehouse significantly.
- Slips, trips, and falls are a very common type of safety hazard that any worker can suffer while working.
- Mishaps occurring while using heavy machinery, heavy materials, and equipment are also unfortunately common.
- Accidents happen at places like docks when forklifts run off the dock, stocks filled in huge boxes fall on employees or any machine or forklifts hit an employee.
- According to OSHA – Occupational Safety and Health Administration created by the American government on December 29, 1970, and signed by President Nixon under the Occupational safety and health administration act, 100 warehouse employees suffer death and 95,000 injured every year in forklift accidents.
- Accidental exposure to harmful substances like fatal gases, concentrated acids, or any substance that can be life taking for humans.
- Improper lifting of heavy materials can cause cramps or irreversible damage to their bodies. They need to be taught the proper way to lift and handle heavy materials.
- Injuries due to moving parts of heavy machinery like cranes and monorails. The workers need to be educated about the functioning of each type of machine.
If you follow the guidelines created by OSHA you can avert unwanted tragedies both for the workers and your warehouse. Here are a few guidelines that we have quoted from OSHA Pocket Guide.
For Operating Forklifts
- Train, evaluate, and certify all operators to ensure that they can operate forklifts safely.
- Follow safe procedures for picking up, putting down, and stacking loads.
- Drive safely, never exceeding 5 mph, and slow down in congested areas or those with slippery surfaces.
- Do not allow anyone under 18 years old to operate a forklift.
- Properly maintain haulage equipment, including tires
- Before using a forklift, examine it for hazardous conditions that would make it unsafe to operate.
- Train employees on the hazards associated with the combustion byproducts of forklift operation, such as carbon monoxide.
- Provide covers and/or guardrails to protect workers from the hazards of open pits, tanks, vats, and ditches.
- Ensure adequate ventilation either by opened doors/windows or using a ventilation system to provide enough fresh air to keep concentrations of noxious gases from engine exhaust below acceptable limits.
- Maintain sufficiently safe clearances for aisles and at loading docks or passages where forklifts are used.
Hazard Communication
It refers to the hazards caused by chemicals that can cause irritation, burns, serious physical hazards, and other types of corrosions.
- Make sure that the workers read the MSDS (Material Data Safety Sheets) and pass on the entire information to the other employees about the corrosive and inflammable chemicals
- Follow instructions on the MSDS for handling chemical products
- Train employees on the risks of each chemical being stored
- Provide spill cleanup kits in any area where chemicals are stored
- Have a written spill control plan
- Train employees to clean up spills, protect themselves and properly dispose of used materials
- Provide proper personal protective equipment and enforce its use
- Store all chemicals safely and securely
- Store chemicals away from forklift traffic areas
Docks Safety Guidelines
While loading and unloading there can be accidents that can happen as mentioned above.
- Drive forklifts slowly on docks and dock plates
- Secure dock plates and check to see if the plate can safely support the load
- Keep clear of dock edges and never back up forklifts to the dock’s edge
- Provide visual warnings near dock edges
- Prohibit “dock jumping” by employees
- Make sure that dock ladders and stairs meet OSHA specifications
Electrical Safety
Shock circuits & electrical accidents at the charging stations and other areas are the cause of many fatal accidents and fires in the warehouse. Ground fault electrical shock is a frequent electrical hazard.
- OSHA requires that employers provide ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) for receptacle outlets
- Warehouses should provide assured equipment grounding conductor programs
- Prohibit smoking and open flames in and around charging stations
- Provide adequate ventilation to disperse fumes from gassing batteries
- Ensure those fire extinguishers are available and fully charged
- Provide proper personal protective equipment such as rubber gloves and eye and face protection
- Properly position forklifts and apply brakes before attempting to change or charge batteries; follow required procedures when refueling gas or propane-fueled forklifts
- Provide conveyors, overhead hoists, or equivalent materials handling equipment for servicing batteries
- Provide an eye washing and safe shower facility for employees exposed to battery acids.
Wall & Floor Openings and Holes To Avoid Free Falls
- Use fall protection like fall restraints. They are the systems that have equipment like guardrails, standard railing, harness, warning lines, etc.
- Fall arrest systems like safety nets are other types of these systems that stop falls.
Respiratory Protection
- The warehouses that deal with toxic gases or the materials that emit toxic gases need to provide their employees with personal protective equipment (PPE)
- OSHA strictly regulates employers to provide their employees with proper PPE
- Many times it’s observed that even though the company provides PPE kits the workers don’t wear them. The use of PPE should be promoted and enforced in facilities where there is a chance of injuries through airborne agents
To know more about safety guidelines, download the OSHA Pocket Guide for safety.
13. Warehouse Order Fulfillment Strategies
All that’s done in a warehouse is for one ultimate thing, orders, but when orders come many times warehouse managers don’t manage those orders effectively. There are certain order fulfillment strategies that need to be followed while managing the warehouse and failure to implement the correct fulfillment process can lead to –
- Damage or loss of the goods
- Delay in deliveries due to faulty fulfillment process
- Wastage of resources and overuse of materials
Proper execution of processes like picking, packing, and shipping will eventually lead to smoother order fulfillment processes.
14. Best Practices for Warehouse Management
It’s always better to list the best practices for warehouse management so that you can have a list that you need to follow while managing your warehouse. Here’s a list of some, never to miss best practices.
Wave Picking and Cross-docking
If you are a businessman who focuses on ROI then you need to manage your warehouse with lean warehouse management techniques. Cross-docking is the best way to significantly decrease the storage and handling costs and time.
If you have complex shipping systems wave picking can be very helpful. Moreover, if you use an advanced tracking method you can extract amazing benefits with cross-docking and wave picking.
Fewer Touchpoints – Less Time Waste
Removing unwanted touchpoints makes the order fulfillment process quicker and easier. Keep only those steps that are necessary as unwanted touchpoints can increase the wear and tear of the products.
Fast selling products should be easy to reach
Inventory analysis procedures like ABC analysis and FNS analysis will help you to figure out the most popular stocks in the warehouse so that you can keep them in the places which are nearer to the packing station or easy to pick and pack to boost the order fulfillment process.
Information sharing is a must
It’s always about how quickly and transparent the information is being shared. In warehouse management, information sharing is crucial with all the stakeholders of the warehouse operations.
Using a warehouse management system can help you in sharing data perpetually and give you more visibility of the warehouse, easy to track products in the warehouse, convenient to make calculations as proper information is shared to all the other accounting and other software.
Plan picking procedures
The picking procedure should be solid because though it seems to be a no big deal but a solid in place picking strategy with an efficient warehouse management system is needed to boost up the perfect order percentages.
Use data to manage your supply levels
First of all, collect as much data you can about the stock levels, stock flows, and everything else and then capitalizes on it by analyzing the data with the help of advanced inventory and warehouse management software to manage the supply chain. With the help of analysis, you can forecast future demands and know when you need to increase the supplies.
“Forecasting takes this a step further — the same camera data can be fed through machine learning algorithms to teach an intelligent stock management system to predict when a resupply will be needed. Eventually, the theory is, warehouses and distribution centers will effectively run themselves with very little need for human interaction.” — Bernard Marr, How Big Data And Analytics Are Transforming Supply Chain Management, Forbes.
Don’t rely on manual input
Let me correctly put it, don’t completely rely on manual input because manual inputs can be deceptive sometimes. Manual entries can always carry errors with them. Instead, you can always use barcode and RFID scanners to record the incomings, outgoings, and other information. Simple point and click to scan products should also be used to track the inventory flow.
You can connect these tags and scanners to warehouse and inventory management software to make sure that everything is updated simultaneously.
However, one must never forget that human help is needed when you need to check that the virtual data is in coherence with the on-ground reality.
One item, One SKU
To keep consistency in the SKUs across vendors, suppliers, inventory and sales are a bit tough but using an automated inventory and warehouse management system will help you consolidate the SKUs to reduce manual errors, increase inventory accuracy, and decrease manual verifications.
Track your warehouse KPIs
Key Performance Indicators are the mirror that will always show a true picture of how your warehouse is performing. You need to keep checking your inventory and warehouse KPIs regularly depending on the nature of your business.
Warehouse safety needs to be prioritized
You need to follow all the safety guidelines proposed by OSHA – Occupational safety and health administration. Read our safety concerns for the warehouse section of this page to know about the safety procedures.
Don’t take safety precautions lightly as ignoring safety concerns can lead to fatal consequences.
Be prepared for emergencies
Contingency plans should be on your priority list as emergencies like natural disasters, data breaches or any mishaps occurring in the facility can come anytime.
Allow 360-degree feedback
360-degree feedback means you accept feedback from everyone and not only from warehouse managers or top officials. Workers working on the ground are the ones who know your warehouse in and out. If there are any issues they will be the ones who will know them first hand.
So, always listen to juniors. They have the best advice and feedback for you.
Iterate on operations
Introspection is a must whenever you implement a plan because blindly sticking to one plan without any iterations can be injurious to warehouse operations. You can never be perfect and hence you need to change and improve your plans and the way you implement your plans.
Auditing and surveying your inventory is a must
Auditing and surveying the inventory from time to time is a habit that you should inculcate in your warehouse managers and workers. An inventory that is equivalent to half of the company’s working capital deserves more attention to the warehouse and its 5 crucial processes – receiving, put-away, picking, shipping, and maintenance that have a major impact on the warehouse’s productivity.
You can use DMAIC: Define, Measure, Improve and Control process and also the PDCA: Plan, Do, Check, and Act process along with the use of a cross-functional team to tackle issues.
Cycle counting and root cause analysis should be your way of approaching the inventory and warehouse surveying and auditing.
You should make accurate percentages of every department available to everyone because inventory accuracy records affect all the stakeholders of the warehouse.
15. Warehouse Management System
A warehouse management system is a software that manages and optimizes inventory other warehouse operations.WMS is considered to be an integral part of any business having a warehouse because to survive in the competitive environment you need to be equipped with every possible software. Moreover, a warehouse management system can help you in scaling up your business without worrying about the management part.
As far as the retail eCommerce industry is considered, it is one of the fastest booming businesses in the U.S. According to the U.S. census department; retail sales rose to 0.7% in July 2019. Department store sales rose by 1.2%.
All these facts and figures indicate the prosperous and fast-paced growth of the eCommerce business.
To have your own firm ground and stand out from the crowd in this competitive field of eCommerce, you clearly need a Warehouse Management System(WMS).
What is WMS?
WMS or warehouse management system, as the name suggests, an affordable A-Z software solution for managing your warehouse. The Software handles inventory visibility, managing supply chain operations alongside integration with a TMS (Transportation management system) or an inventory management system.
Why should I move from excel to a WMS?
It may be like this that you are already using excel to manage your warehouse. Then you may ask, “Why should I change to WMS? Well, here are the possible WHY’s that might help you.
Manual Input and Output
Working with spreadsheets means manual input of data. It costs both time and money. As the company gets bigger in size, more and more people are assigned to do the same repetitive work that can easily be automated using WMS.
Input Errors
If the inputs are done manually, then Faulty spelling, missing out to fill a particular field, filling incorrect data, etc. are inevitable. Spreadsheets don’t have built-in business logic to prevent such errors.
Lack of Real-Time
Working with spreadsheets is not at all an enjoyable task. It is not frequently maintained, which means data is not always up to date. As a result, decisions are often taken based on the existing old and obsolete data.
Why do we need a WMS to manage warehouses?
As per a warehouse survey done by Motorola Solutions Future, only 26% of company managers view warehouses and distribution centers as an asset that can drive growth for their business. Clearly, a lot of people are not visionary enough to understand the importance of warehouse management.
Implementing WMS within an organization can help drastically in reducing labor costs, omitting human errors, and improving inventory accuracy, improving customer service, and error-free picking and shipping goods. Modern-day warehouse management systems operate on real-time data; this allows the organization to manage all current activities like orders, shipments, receipts, etc. within one single platform.
According to an eCommerce fulfillment report, only 20% of businesses are implementing a warehouse management system; 10 % don’t have any experience with using a WMS, whereas 7% of them are not sure of the benefits it can offer.
Let’s have an in-depth understanding of the benefits of WMS in the retail industry.
Advantages of WMS in the Retail Industry
| 1. Inventory Control | 4. Improved Capacity |
| 2. Labor Productivity | 5. Reduced Operational Costs |
| 3. Transparency and Visibility |
Inventory Control
A WMS gives organizations the ability to track inventory across multiple warehouse locations, in various distribution centers and stores.WMS also maintains a record of every warehouse slot/bin location along with the items that have been stored in it.
According to a survey,
34% of businesses are shipping late due to unavailability of products in stock,
With real-time information, WMS provides quick and accurate feedback. This helps companies to respond quickly to their customer’s demands while distributors and wholesalers know precisely what is in the warehouse and when it needs to be replenished.
Labor Productivity
In a survey, when asked, “How does your business cope with fulfillment during your busiest periods?”
“45% said that they paid overtime for the existing staff.”
While on the other hand
“38% reported having pulled staff from other parts of the business.”
This is certainly not the best way to cope up with the busiest hours or managing your employees.
WMS here comes to your rescue. WMS increases the productivity of labor by managing worker tasks. It can select tasks from a queue of all pending activities and set the priority of the tasks.
Apart from this, WMS also provides labor planning feedback to management. Based on order loads, WMS can estimate the number of personnel needed to complete the day’s activities.
Transparency and Visibility
Won’t it be great if your supplier could access their own inventory in your warehouse alongside with on-hand SKU?
By shedding some redundancy, your suppliers could minimize the costs associated with holding excess warehouse inventory.
WMS also provides complete visibility of what’s going on inside your warehouse. Rather than periodic reports, where the inventory count is taken only at the end of the accounting period; WMS provides perpetual reports that enable continuous monitoring of your inventory.
Improved Capacity
23% of businesses increase their warehouse capacity to cope with their sales growth, a survey reveals.
Isn’t it an optimal solution to manage your existing warehouse rather than spending on increasing warehouse capacity?
Warehouse Management Systems can also improve warehouse capacity. This is done by allowing goods to move effortlessly through the facility.
WMS provides accurate information with zero information lead times. This allows you to reduce inventory levels which in turn increases inventory turn rate.
Reduced Operational Costs
26% revealed their pain points as finding time for tidying / upkeeping.
The right WMS can help you in reducing waste by identifying perishable and date-restricted stock in your warehouse which needs to be picked first. WMS can calculate the optimum location for each item that helps inefficient use of warehouse space with minimal pick and put away effort.
According to the survey,
“38% reported having pulled staff from other parts of the business.”
Using a WMS reduces your on-hand inventory, optimizing space, and reduces the need to allocate valuable resources from other parts of the supply chain to more employees to cope up with the busiest periods.
How is it different from Inventory Management Software?
Similarity |
Differences |
|
Both WMS and IM involve monitoring on the product level. Example tracking products with barcodes, cycle counting, picking, packing, and shipping, etc.
|
WMS is more complex than IM. WMS is more focused on the operations of business warehouses. Example: dividing warehouse into compartments or bins, allocating optimum location for storage of frequent on the go items or perishable items, etc
IM is more product detailed oriented and not focused on what is there in the warehouse. Example: product details, product SKU, the quantity of the items, batch, where the items are located within multiple warehouses, etc.
|
How to select a Warehouse Management System?
Calculate ROI
The more daily transactions – such as moving pallets and picks, locating different items in warehouses, maintaining incoming and outgoing items from the warehouse, etc., the greater the potential for ROI.
Must have a User-Friendly UI
Even with all the advanced functions available in your WMS, if it’s not user-friendly, you and your staff won’t be able to get the maximum out of the software.
Asking relevant questions before investing in a WMS really helps. For example:
- Does this system enable me to easily sort and view all the necessary information?
- Is the navigation model of the WMS easy to use and understand?
- Can the software provide a real-time window into your warehouse operation with only a few clicks?
Automation
Look for WMS that supports wireless technologies and where the tedious repetitive operational processes can be automated. Opt for a system that promises real-time delivery, i.e., inventory is updated as soon as the new data is entered, and not with the periodic batch.
Integration with Accounting Software and Shipping Partners:
Real-time integration with your accounting software and shipping partners reduces transcription errors at your back office, lowers the requirement of staff, and improves the access to information throughout your organization.
Inquire about system capacity
It is important to ensure if your WMS can be upgraded in the near future. This avoids the need to purchase new systems within a short period of time, not to mention the loss of valuable time of the organization with experiments. Questions that can still be asked are
- What is the maximum number of users that can work in WMS at any given time?
- What if you want to add another warehouse and want to manage multiple warehouses?
Ask about Technical Support
Even if everything may look as simple as “2+2=4”. Sometimes, life can hit you hard with complex puzzles. After acquiring the software, you can bump into problems that can’t be solved internally. You may need to rely on the software vendor’s technical support team. Find out if there is a provision for after-sales tech support. Ask about the policies for maintenance, upgrades, and support.
Future of WMS in the retail industry
In most warehouses, daily activities and processes are still performed manually. However, new emerging technologies such as drones, robots, IoT, AR & VR will transform the world of warehousing within the coming years. Here’s how –
According to Westernacher Consulting,
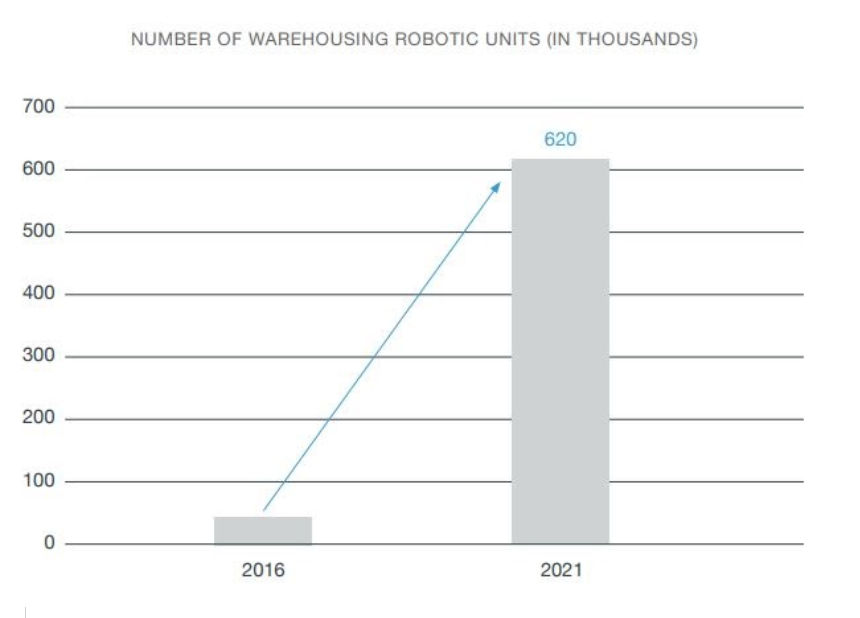
“Worldwide spending on warehouse automation technology has already topped $2 billion and is expected to reach $22.4 billion by 2021.”
Warehouse automation may be the key to finding a solution to tedious warehouse distribution challenges. Thousands of businesses worldwide have adopted this solution. In a nutshell, warehouse automation allows you to achieve excellent outcomes with minimal effort. This is achieved by the use of one or more than emerging technology.
A quick question that you may have, “Why do I need warehouse automation?” Here are quick 5 Points for considering automation.
- reducing overhead and operating expenses
- increasing efficiency and productivity
- Minimizing manual processes
- Maximizing warehouse space utilization
- Synchronizing the material handling equipment
Warehouse Automation can be subdivided into two parts: Process Automation and Physical Automation.
Process automation
Process Automation, as the name suggests, is the digitalization of the manual process like inventory data collection and integrating the data in the cloud platform. WMS being a cloud software is a perfect example of process automation.
Physical Automation
It includes various forms of robots and drone systems in the warehouse. Physical Automation is more costly to implement. This type of automation only provides a reasonable Return on Investment (ROI) for larger high-volume warehouses.
Drones
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones, can be used in the up-gradation of the warehousing processes. Aerial Drones with the help of optical sensors can locate an item in a warehouse from a distance as large as 10 meters. Together with the Warehouse Management System, this will provide fast detection of individual items and prevents inventory mismatches.
Robots
Companies like Amazon have implemented packaging robots.
Amazon is using the new robots known as CartonWrap from Italian firm CMC Srl has the capacity to pack 600 to 700 boxes per hour. This is roughly four to five times the efficiency of its human counterpart. Apart from CartonWrap, the company also announced its intended use of another robot known as SmartPac, which will automate the process of mailing items in patented envelopes.
16. Warehouse Reports
Reporting and analysis of the reports are very crucial for any business. Reports will tell you how your warehouse and employees are responding to the strategies. Are you able to achieve the targets or not? Even if the business is running great you need to study the reports to find out the needs of the warehouse and figure out any possible malfunctioning.
There are three types of reports –
Bulk Picking Report / Picklist
The report majorly talks about the picklists and bulk picking products and the efficiency of the picking and the number of picklists generated every day. It is a crucial report that encloses much information about the warehouse and business performance.
Empty Bin Report
We cannot rely merely on visual inspection when it comes to tracking empty bins. Moreover, the superfast supply chains also make it imperative to know which containers are empty and which ones will get emptied in the near future. This data is required for smooth planning and capacity estimation.
Inventory on Hand Report
Inventory on Hand Report again is an important report that will perpetually tell you the amount of inventory available to sell so that you build your sales strategies accordingly.
To read more about the reports, their uses, and calculations in detail click here.
17. Own Warehouse vs. 3PL
There is always a dilemma a budding businessman goes through, whether to keep owning his warehouse or shift his/her fulfillment centers to a 3PL company. If you also are having trouble with making a correct decision for your business, then read the below-given information about Own warehouse vs. 3PL.
Own Warehouse |
3PL |
|
Control
Own warehouse means control over the supply chain, how the products are warehoused, and how the products are delivered to the customers. It’s you who will decide how the products will flow through the warehouse to the customer by providing different solutions for different problems.
|
Control
3PLs don’t offer that much control over your fulfillment processes because they have a one-size-fits-all solution for every company they cater to.
|
|
Customizable Experience for Your Customers
You can provide your customers the experience they want and innovate in that too. You can ask your customers to send in the requests and you can customize your products accordingly and charge for that extra too
|
Not that much freedom
Most of the 3PLs do not offer that level of freedom to the companies. You can’t take over the packing and shipping processes for your products.
|
|
There is a lot of minute and major costs that you have to bear to set up your own warehouse.
|
You don’t have to worry about setting up the infrastructure, managing workload and maintenance, and start-up costs.
|
|
You have to be your own expert or hire one
You have to hire warehouse experts or learn by trial and errors
|
Proven Experience and expertise
You can rely on 3PLs expertise in warehouse operations for shipping, picking, packing, and demand forecasting.
|
|
Tough to integrate different channels
It’s not that tough if you have knowledge of how to manage a warehouse with warehouse management software. Many warehouse management system companies offer training and support in using warehouse management software efficiently.
|
Easy to integrate different channels
3PLs have the industry’s best picking packing and shipping technologies along with warehouse management systems because they serve many companies and hence they have to be the best.
|
|
Tough to relocate to decrease lead time
You have to invest more in opening different warehouses in the locations where you have a strong customer base.
|
Easy to shift the fulfillment stock to reduce lead time
Decrease order lead time by easily relocating, on the other hand, 3PLs give you a chance to shit your products to a center that is nearer to the geographical location where you have more sales. Doing this can help your delivery order in shorter lead times, in fact on the same day.
|
|
Tough to scale up
Scaling your business requires some tough investment decisions to be taken because you will require more workforce, space, and everything needed to scale up
|
Easy to scale up
|
|
Innovate on your own
You are all by yourself to innovate. However, having said that you can implement the innovations that you want
|
Professionals innovate for you
3PLs work for different types of industries and hence they are always innovating and evolving and they can also offer you some really good innovative ideas to improve your business. For example, they can tell you about effective procurement methods or shipping and handling methods.
|
|
The SG & A cost
The selling, general and administrative costs are high in their own warehouse because there is a cost of the management of the entire facility and workers. Though in the longer-term it turns out to be lesser than the money invested in 3PLs
|
Reduce the SG & A cost
Selling, general and administrative costs are decreased initially for small and medium businesses because your day-to-day operations are simplified in a 3PL company. So, even if you are planning to scale up SG & A cost is considerably low, unless you become a huge company with a vast geographical coverage
|
|
You can include any number of SKUs
Since it’s your own warehouse you can include any number of SKUs and won’t have to bother
|
There is a charge for every new SKU added
3PLs charge for every new SKUs so you have to be meticulous about which line of products you want to add and whether those products will bring returns or not
|